| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- Recoil
- react
- Render Queue
- 좋은 PR
- docker
- Microtask Queue
- 25년 2월
- linux 배포판
- Custom Hook
- Headless 컴포넌트
- Sparkplug
- jotai
- helm-chart
- AJIT
- zustand
- 암묵적 타입 변환
- JavaScript
- 명시적 타입 변환
- 타입 단언
- CS
- type assertion
- 프로세스
- useLayoutEffect
- 클라이언트 상태 관리 라이브러리
- mocking
- TypeScript
- prettier-plugin-tailwindcss
- Compound Component
- 회고
- msw
- Today
- Total
구리
TIL_210323_상속, 오버라이딩 본문
<오전수업>
상속
상속이란 ? 부모 클래스로부터 자원을 물려받아 자식 클래스가 자원을 사용할 수 있도록 해주는 개념으로 private 멤버와 생성자는 상속이 불가하다.
상속을 받게 되면 부모 클래스 그 자체의 상속이 아닌 부모 클래스의 객체를 상속 받는다는 표현이 더 적절하다.
super()
조상생성자 호출시 사용되며, 생성자에 부모 생성자 호출시 무조건 첫줄에서만 사용한다.
(조상생성자가 없으면 컴파일러가 자동으로 super() 를 생성한다)
오버라이딩 기법
부모로부터 상속받은 메서드의 내부(구현부)를 자식이 재정의한 메서드로 오버로딩과 헷갈리지 않도록 한다.
오버라이딩 : 부모로부터 상속 받은 메서드의 내용을 변경하는 것 (modify, change)
오버로딩 : 기존에 없는 새로운 메서드를 추가하는 것 (new)
아래는 상속, 오버라이딩, super() 생성자를 사용한 예시다
부모클래스인 ParentClass
package com.bjy.ext;
public class ParentClass {
String s = "";
public boolean b =true;
private char c = 'M';
// private 이기에 다른 클래스에서 직접 접근 불가
// public인 메서드를 생성하여 privte 변수에 접근할 수 있게 한다 (캡슐화)
// getter / setter 메서드 생성
// 기본 생성자
public ParentClass() {
this.setC('F');
this.test();
System.out.println("ParentClass 생성자 내에서 출력");
}
// 매개변수 생성자
public ParentClass(String s) {
this.s = s;
System.out.println(s);
}
// getter 메서드
public char getC() {
return c;
}
// settet 메서드
public void setC(char c) {
this.c = c;
}
public void sum(int n1, int n2) {
System.out.println(n1 + n2);
}
// ChildClass 인스턴스 생성해도 같은 클래스가 아니라서 접근 불가
// 오로지 ParentClass만 접근 가능
private void test() {
System.out.println("private 메서드 호출");
}
}ParentClass를 상속받은 ChildClass이다. (ParentClass의 객체를 상속받는다)
package com.bjy.ext;
public class ChildClass extends ParentClass {
String child = "자식변수";
public float f = 1.45f;
// 기본 생성자
public ChildClass() {
// 생성자에서 다른 생성자 호출시 무조건 첫줄에서 사용 !
super("test"); // super(); 도 가능함
super.sum(20, 30);
System.out.println("ChildClass 생성자 내에서 출력");
}
// 부모클래스의 메서드 오버라이딩 (메서드 선언부는 그대로, 구현부만 변경한다)
public void sum(int n1, int n2) {
System.out.printf("%d와 %d의 합은 %d입니다.", n1, n2, n1+n2);
}
}
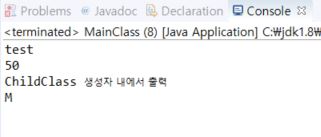
MainClass에서 ChildClass의 인스턴스를 생성하면 다음과 같은 결과를 얻는다.
package com.bjy;
import com.bjy.ext.ChildClass;
import com.bjy.ext.TestClass2;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChildClass cc = new ChildClass();
// System.out.println(cc.child);
// child의 접근제한자는 default이기에 같은 패키지에서만 접근 가능
System.out.println(cc.getC());
}
}
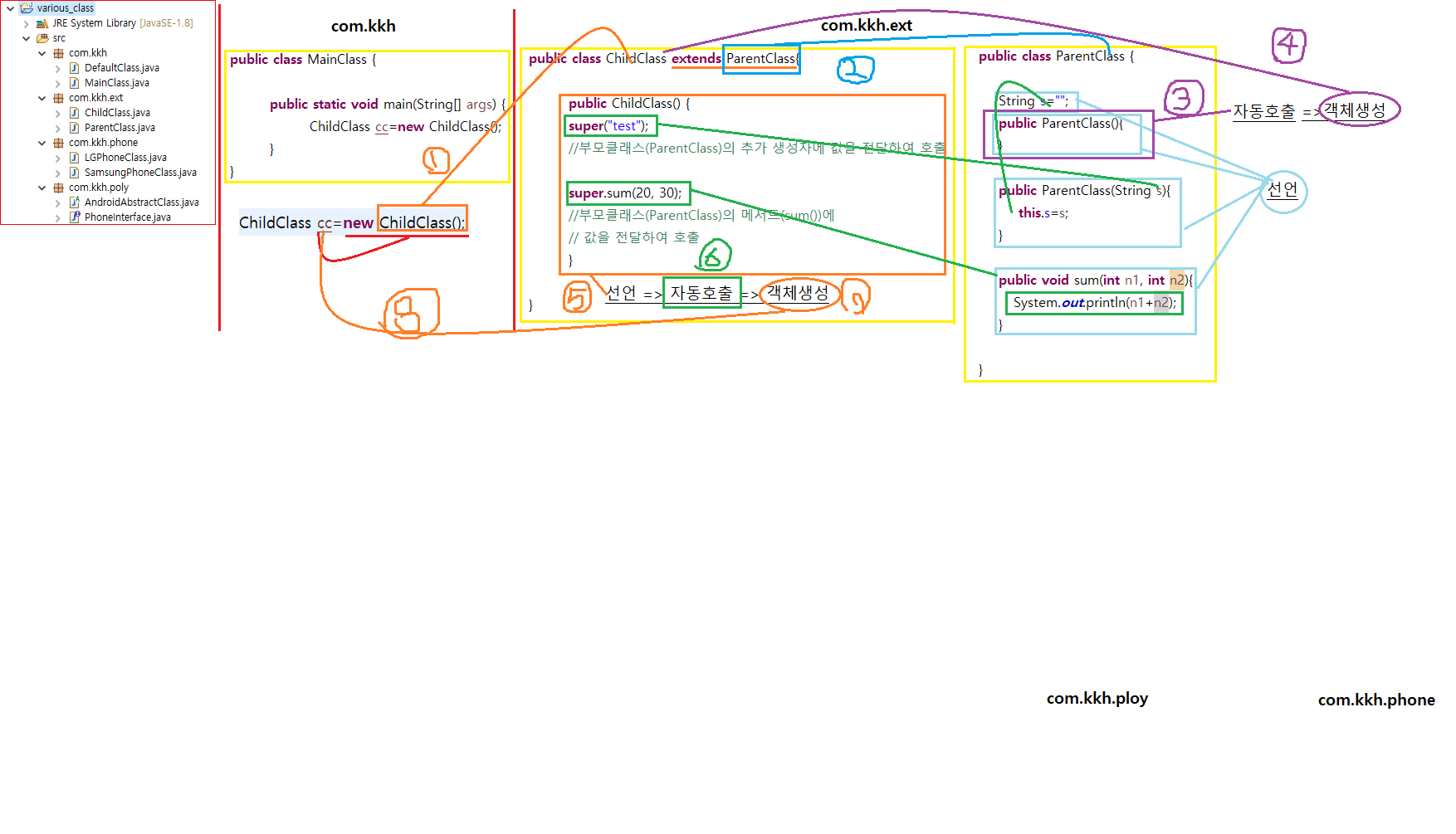
상속된 클래스 객체 진행 과정
만약 MainClass에서 ChildClass cc = new ChildClass(); 작성하였을 때 객체 생성 진행 과정이다.
1. ChildClass(); 실행
1-1. MainClass와 동일 패키지내 ChildClass 파일 검색, 없으면 전체 패키지(public) 검색
1-2. ChildClass 파일내 선언부 확인 (상속받은 것이 있는지) public class ChildClass extends ParentClass
1-3. extends ParentClass 부모클래스 확인 후 파일 검색
ParentClass 파일내 선언부 확인
상속 키워드 없을 경우 클래스명(ParentClass) 확인
클래스(ParentClass) 내부를 선언 (변수, 생성자 등..)
생성자 호출
객체 생성 : new ParentClass();
extends 키워드에 의해 ChildClass에서 상속 ----- extends ParentClass 완료
2. 클래스명(ChildClass) 확인
3. ChildClass 내부를 선언
4. ChildClass의 생성자 호출
5. ChildClass 객체 생성 ---- new ChildClass(); 완료
<오후수업>
문제
사전 준비 작업:
1. C 드라이브 의 filetest 폴더에 bookdata.txt 파일과 bookImages 폴더가 존재해야 합니다
bookdata.txt : 첨부파일을 넣어 놓고,
bookImages 폴더 : 첨부파일을 압축 푸시면 됩니다.
프로젝트 생성(같은 패키지 내에서 클래스 생성) :
1. MainClass : 전체 흐름을 담당 (일종의 Controller) / main() 포함
2. PressClass : 출판사(String press), 저자명(String author) 변수를 보유 (해당 변수들은 모두 외부 접근 불가!!!)
3. BookClass : 제목, 가격(int형), 이미지파일, 할인율(int형) 변수를 보유 (해당 변수들은 모두 외부 접근 불가!!!)
(PressClass 상속 받는다)
4. DataClass : 전체 데이터를 보유
5. MethodClass : 실행 메서드들만 보유, 해당 메서드들은 객체 생성 없이 사용할 수 있도록 선언
MethodClass 메서드
5-1. readBooksData(String uri) : 읽어들일 문서의 경로와 파일정보 (bookdata.txt)을 전달 받아 DataClass타입객체에 저장
5-2. makeBooksHTML() : html 태그들을 생성하여 문자열로 저장
6. PrintClass : 출력 전용 클래스로 "c:/filetest/bookList_test.html" 파일을 생성하는 역할 담당 (객체 생성없이 사용함)
PrintClass 메서드
6-1. PrintHTML(tags, url) : 태그명, 저장 경로 및 파일명을 전달하여 html 파일 완성하는 메서드
PressClass
package com.bjy;
public class PressClass {
private String press="";
private String writer="";
public PressClass() {}
public PressClass(String press, String writer) {
this.press = press;
this.writer = writer;
}
/* 외부로부터 저자명, 출판사명을 추출할 수 있도록 각각의 getter 메서드 선언 */
public String getPress() {
return press;
}
public String getWriter() {
return writer;
}
}BookClass
package com.bjy;
public class BookClass extends PressClass {
private String title="";
private int price=0;
private String image="";
private int discount=0;
public BookClass() {}
public BookClass(String press, String writer, String title, String price, String image, String discount) {
super(press, writer);
this.title = title;
this.price = Integer.parseInt(price);
this.image = image + ".jpg";
this.discount = Integer.parseInt(discount);
}
/* 외부로부터 데이터를 추출할 수 있도록 private 변수의 getter 메서드 선언*/
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public String getImage() {
return image;
}
public int getDiscount() {
return discount;
}
/* 객체 보유하고 있는 값을 쉽게 출력하기 위한 메서드 선언*/
public void testToString() {
System.out.println(this.title + "-" + super.getWriter() +
"-" + super.getPress() + "-" + this.image + "-" +
this.price + "-" + this.discount);
}
}DataClass
package com.bjy;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DataClass {
public static ArrayList<BookClass> book = new ArrayList<BookClass>();
public DataClass() {
/* 만약 DataClass의 생성자에서 books에 데이터 추가시킬 경우
* static이 있더라도 반드시 DataClass 객체 생성해야한다.
* 이유 : 생성자는 객체 생성시 자동호출되기 때문이다.
*/
}
}MethodClass
package com.bjy;
import java.io.*;
public class MethodClass {
public MethodClass() {
}
/** MainClass의 main() 내부로부터 읽어들일 파일의 경로, 이름 전달받아 **/
/** DataClass의 멤버(ArrayList)에 추가 **/
public static void readBooksData(String uri) {
FileReader fr = null; // 파일 읽기
BufferedReader br = null; // 한줄씩 읽는 readLine() 보유
BookClass o = null; // DataClass의 books에 추가할 객체
String one = ""; // 한줄씩 저장할 때 사용할 변수
String[] tmp = null; // split으로 쪼갠 결과 저장할 변수
try {
fr = new FileReader(uri);
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
while( (one=br.readLine()) != null ) {
tmp = one.split("__");
o = new BookClass(tmp[0], tmp[1], tmp[2], tmp[3], tmp[4], tmp[5]);
o.testToString();
DataClass.book.add(o);
}
}catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("파일 읽기 ERROR : " + e.getMessage());
}
} // end of readBooksData()
/** DataClass의 멤버(ArrayList)에 추가된 데이터 이용하여 **/
/** 실제 html 파일의 내부 태그들 완성 **/
public static String makeBooksHTML() {
int rowCount = DataClass.book.size();
String tags = "";
tags = tags + "<!doctype>";
tags = tags + "<html>";
tags = tags + "<head><title>News Stand</title></head>";
tags = tags + "<body>";
tags = tags + "<table border='1'>";
tags = tags + "<tr>";
tags = tags + "<td>책표지</td>";
tags = tags + "<td>제목</td>";
tags = tags + "<td>저자</td>";
tags = tags + "<td>출판사</td>";
tags = tags + "<td>정가</td>";
tags = tags + "<td>할인율</td>";
tags = tags + "</tr>";
//for(BookClass bc : DataClass.book) 가 훨씬 간편해
for(int n=0;n<rowCount;n++) {
tags = tags + "<tr>"; // 행 시작
tags = tags + "<td>"; // 열 시작
tags = tags + "<img src='./bookImages/" + DataClass.book.get(n).getImage() + "' />";
tags = tags + "</td>"; // 열 닫기
tags = tags + "<td>"; // 열 시작
tags = tags + DataClass.book.get(n).getTitle();
tags = tags + "</td>"; // 열 닫기
tags = tags + "<td>"; // 열 시작
tags = tags + DataClass.book.get(n).getWriter();
tags = tags + "</td>"; // 열 닫기
tags = tags + "<td>"; // 열 시작
tags = tags + DataClass.book.get(n).getPress();
tags = tags + "</td>"; // 열 닫기
tags = tags + "<td>"; // 열 시작
tags = tags + DataClass.book.get(n).getPrice()+"원";
tags = tags + "</td>"; // 열 닫기
tags = tags + "<td>"; // 열 시작
tags = tags + DataClass.book.get(n).getDiscount()+"%";
tags = tags + "</td>"; // 열 닫기
tags = tags + "</tr>"; // 행 닫기
}
tags += "</table>"; // 테이블 닫기
tags += "</body>"; // 사용자에게 보여지는 부분 종료
tags += "</html>"; // html 전체 문서 종료
return tags;
}
}PrintClass
package com.bjy;
import java.io.*;
public class PrintClass {
public PrintClass() {
}
public static void PrintHTML(String tags, String uri) {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(uri);
fw.write(tags);
}catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("파일 쓰기 오류 : " + e.getMessage());
}finally {
try {
fw.close();
/* 파일 닫기는 정상작동이 되든, 오류가 발생하든 항상 해야 하기에
* finally 구문에 넣고 try-catch문 한번 더 사용
*/
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("파일 저장 오류 : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}MainClass
package com.bjy;
import java.io.File;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String uri = "c:/filetest/bookdata.txt";
MethodClass.readBooksData(uri);
String tags = MethodClass.makeBooksHTML();
// 완성된 태그 확인용, 확인 후 코드 삭제
System.out.println(tags);
String url = "c:/filetest/bookList_test.html";
PrintClass.PrintHTML(tags, url);
}
}
느낀점
머릿속에서 큰 크림을 그리고 코드를 짜는 것보단 직접 그림을 그려가며 클래스 간의 흐름과 관계를 순서화하고 클래스마다 메서드만 작성 후 메서드가 하는 역할들을 주석처리해주고 필요한 매개변수나 지역변수, 클래스의 변수들을 미리 작성해보고 코드를 짜는 것이 훨씬 더 윤곽이 잘 잡혔다.
직접 코드를 짜는 과정에선 DataClass의 멤버변수에 public 접근 제한자를 붙이지 않고 작성하여 씨름하였다. 접근 제한자도 신경 써서 코드 작성하는 것을 기억하자.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TIL_210324_추상클래스, 라이브러리 추가, 엑셀파일 다루기 (0) | 2021.03.24 |
|---|---|
| 이클립스_자바 라이브러리 추가 (0) | 2021.03.24 |
| Bubble Sort : 거품 정렬 (0) | 2021.03.22 |
| 자바의정석_연산자(Operater) (0) | 2021.03.22 |
| 자바의정석_변수(Variable) (0) | 2021.03.22 |


